- Home
- About Us
- Services
- Treatments
- Acid Reflux
- Allergic Rhinitis
- Alcoholic Fatty Liver
- Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Anxiety / Stress
- Arthritis
- Asthma
- Cervical Spondylitis
- Celiac Infection
- Colitis
- Constipation
- Dermatitis
- Detox Programme
- Diabetes (Madhumeha)
- Hair Fall
- Headache
- Hormonal Imbalance
- Hypertension
- Insomnia
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Lungs Disease
- Migraine
- Neurological Disorder
- Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver
- Obesity Management
- Pain Management
- PCOD
- PCOS
- Sciatica Pain
- Sinusitis
- Skin Disorder
- Slip Disc
- Stress Management
- Thyroid
- Weight Management
- Techno-Ayurveda
- Media
- Blog
- Contact Us
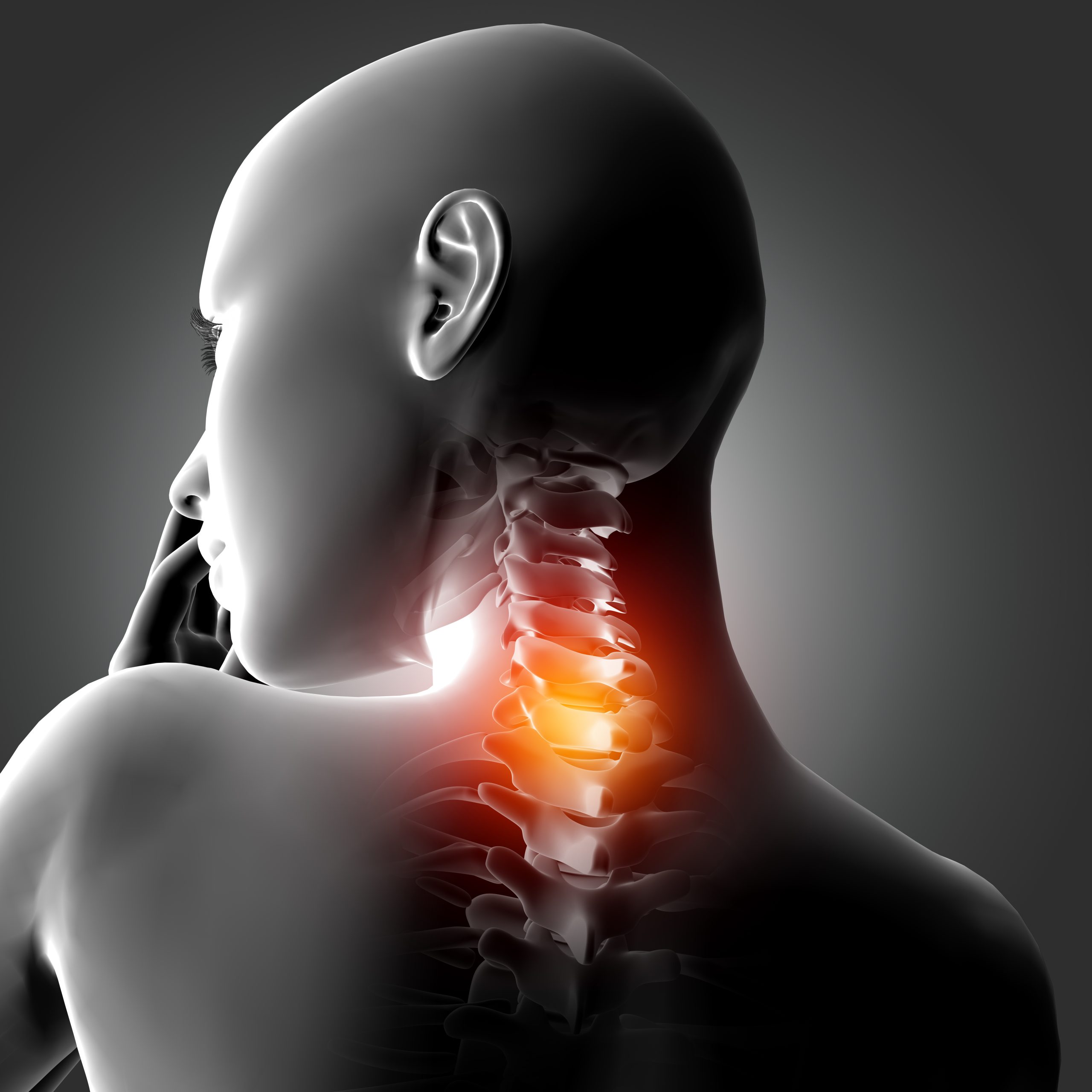
Cervical Spondylitis
Understanding Cervical Spondylitis
According to Ayurveda, cervical spondylitis is caused by the accumulation of Ama (toxins) in the neck region due to impaired digestion or poor lifestyle choices. These toxins cause the body’s tissues to become imbalanced, leading to stiffness, pain, and degeneration of the bones and joints. The imbalance of Vata dosha plays a major role in the condition, as it governs joint movement and flexibility. When Vata is aggravated, it leads to dryness, pain, and stiffness in the bones and muscles.
Additionally, Pitta and Kapha doshas can also contribute to the condition. Pitta imbalances may lead to inflammation, while Kapha imbalances may contribute to fluid retention or sluggish circulation, further aggravating the condition.
Symptoms of Cervical Spondylitis
1. Neck Pain
2. Stiffness
3. Headaches
4. Tingling or Numbness in Limbs
5. Weakness in Muscles
Common Causes of Cervical Spondylitis

Aging and Wear
Cervical spondylitis is primarily caused by aging and natural wear and tear on the cervical spine. As we age, intervertebral discs lose moisture, becoming less flexible, while bone spurs may develop, leading to nerve compression and neck pain.
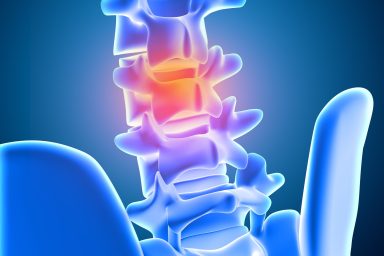
Disc Issues
Cervical spondylitis can be caused by disc issues, such as degeneration or herniation. As intervertebral discs lose water content and elasticity with age, they may shrink or bulge, leading to nerve compression, pain, and stiffness in the neck.
Bad Posture and Strain
Bad posture and repetitive neck strain can contribute to cervical spondylitis by placing excessive stress on the cervical spine. Poor posture, such as slouching or craning the neck forward, accelerates disc degeneration and increases the risk of nerve compression.

Genetics at Play
Genetics can play a role in cervical spondylitis by influencing the susceptibility to disc degeneration. Individuals with a family history of spine problems may inherit genes that predispose them to earlier disc wear, leading to increased risk of cervical disc issues.
Neck Injuries Impact
Genetics can influence how the body heals from neck injuries, with some individuals inheriting a predisposition for slower or inadequate recovery. This may lead to lasting damage, such as accelerated wear of cervical discs, increasing the risk of cervical spondylitis.
Panchakarma Ayurvedic Treatment for Cervical Spondylitis
Cervical spondylitis, also known as cervical spondylosis, is a degenerative condition affecting the cervical spine (neck), leading to pain, stiffness, and potential nerve compression. In Ayurveda, cervical spondylitis is often linked to Vata dosha imbalance, causing dryness, stiffness, and degeneration in the tissues of the neck. Panchakarma, a comprehensive detoxification and rejuvenation therapy, offers an effective approach to manage cervical spondylitis by addressing the root cause—imbalance in the doshas—and restoring the body’s natural harmony.
Panchakarma Treatments for Cervical Spondylitis:
Abhyanga (Ayurvedic Oil Massage): Abhyanga, a therapeutic oil massage, is used to deeply nourish the body and relieve stiffness in the muscles and joints. Medicated oils, especially those with Vata-balancing properties (like Mahanarayan oil), are applied to the neck and shoulders to reduce pain, inflammation, and muscle tension. This therapy improves blood circulation, relaxes the muscles, and enhances flexibility in the neck and spine.
Shirodhara: Shirodhara involves gently pouring warm medicated oil or herbal decoctions onto the forehead, inducing deep relaxation and calming the nervous system. This treatment not only reduces mental stress but also helps relax the neck muscles, relieving tension caused by cervical spondylitis. It enhances blood circulation to the head and neck, which can alleviate stiffness and discomfort.
Swedana (Steam Therapy): Swedana is a form of steam therapy that helps open up the pores and release toxins from the body. By applying gentle heat to the body, this treatment increases circulation, reduces stiffness, and alleviates pain in the neck and shoulders. It can also help improve joint flexibility by promoting the release of toxins that contribute to inflammation.
Basti (Medicated Enemas): Basti is one of the most important treatments in Panchakarma for balancing Vata dosha. Medicated enemas are used to cleanse the lower digestive tract, allowing the body’s natural detoxification process to work more effectively. By reducing Vata imbalances in the body, Basti can help relieve pain and stiffness associated with cervical spondylitis, as it works from the root cause of the condition.
Kati Basti: Although typically used for the lower back, Kati Basti (a therapy involving the application of warm medicated oil to the back) can also be adapted to treat cervical spondylitis. A reservoir of warm oil is placed on the affected area (the cervical spine), promoting deep relaxation, improving circulation, and reducing inflammation in the neck muscles and joints.
Nasya (Nasal Therapy): Nasya is an Ayurvedic treatment that involves administering medicated oils or herbal powders through the nostrils. It is beneficial for relieving sinus and head-related issues, but it also helps reduce the Vata imbalance in the head and neck, thereby easing tension and stiffness associated with cervical spondylitis.
Diet and Lifestyle Recommendations:
- Anti-inflammatory Foods: Incorporating foods like ginger, turmeric, garlic, and ghee into the diet can help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Vata-pacifying Diet: Foods that are warm, moist, and grounding help balance Vata. Avoid cold, dry, and rough foods that aggravate Vata.
- Adequate Hydration: Drinking warm water throughout the day helps keep the tissues hydrated, improving flexibility and reducing stiffness.
- Regular Exercise: Gentle yoga and stretching exercises focusing on neck flexibility can complement the healing process and prevent stiffness from recurring.
FAQs of Cervical Spondylitis
Cervical spondylitis, also known as cervical spondylosis or degenerative neck disease, is a condition where age-related wear and tear affects the cervical spine, leading to neck pain, stiffness, and sometimes nerve compression.
Cervical spondylitis is primarily caused by the natural aging process, where intervertebral discs lose moisture and flexibility, and the bones of the neck develop bone spurs. Other factors like poor posture, repetitive neck strain, and previous injuries may accelerate the condition.
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, patient history, and imaging tests such as X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans to assess the degree of disc degeneration, bone spurs, or nerve compression in the cervical spine.
